Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Thyroid
- Frequency of TERT Promoter Mutations in Real-World Analysis of 2,092 Thyroid Carcinoma Patients
- Heera Yang, Hyunju Park, Hyun Jin Ryu, Jung Heo, Jung-Sun Kim, Young Lyun Oh, Jun-Ho Choe, Jung Han Kim, Jee Soo Kim, Hye Won Jang, Tae Hyuk Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(4):652-663. Published online July 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1477
- 3,666 View
- 194 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) promoter mutations are associated with increased recurrence and mortality in patients with thyroid carcinoma. Previous studies on TERT promoter mutations were retrospectively conducted on a limited number of patients.
Methods
We prospectively collected data on all consecutive patients who underwent thyroid carcinoma surgery between January 2019 and December 2020 at the Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. We included 2,092 patients with thyroid carcinoma.
Results
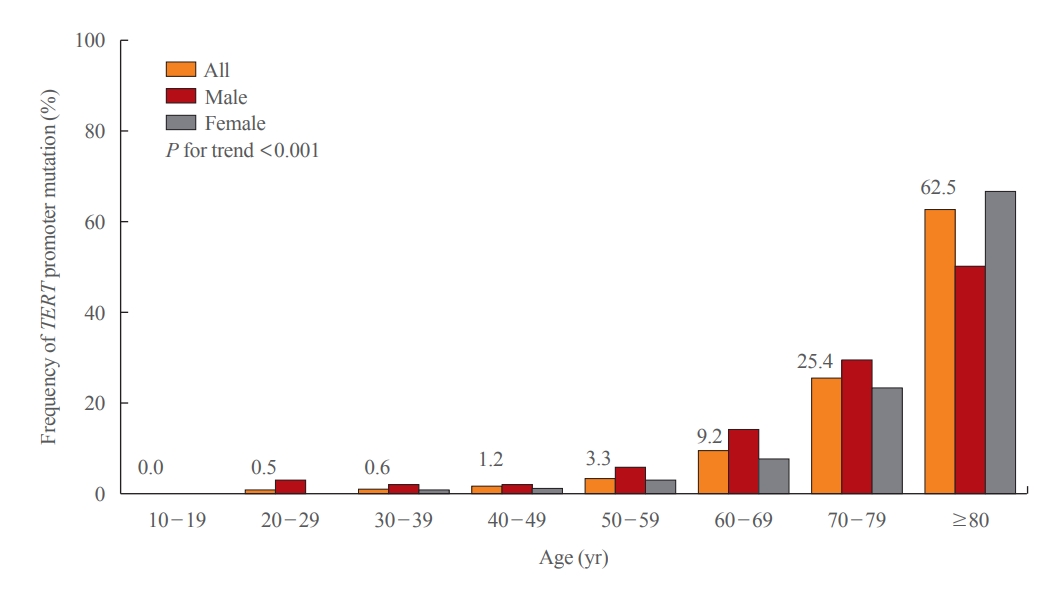
Of 2,092 patients, 72 patients (3.4%) had TERT promoter mutations. However, the frequency of TERT promoter mutations was 0.5% in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (PTMC) ≤1 cm and it was 5.8% in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) >1 cm. The frequency of TERT promoter mutations was significantly associated with older age at diagnosis (odds ratio [OR], 1.12; P<0.001), larger primary tumor size (OR, 2.02; P<0.001), and aggressive histological type (OR, 7.78 in follicular thyroid carcinoma; OR, 10.33 in poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma; OR, 45.92 in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma; P<0.001). Advanced T stage, advanced N stage, and distant metastasis at diagnosis were highly prevalent in mutated thyroid cancers. However, initial distant metastasis was not present in patients with TERT promoter mutations in PTMC. Although the C228T mutation was more highly detected than the C250T mutation (64 cases vs. 7 cases), there were no significant clinicopathological differences.
Conclusion
This study is the first attempt to investigate the frequency of TERT promoter mutations in a real-world setting. The frequency of TERT promoter mutations in PTC was lower than expected, and in PTMC, young patients, and female patients, the frequency was very low. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by-
TERT Promoter Mutations Frequency Across Race, Sex, and Cancer Type
Talal El Zarif, Marc Machaalani, Rashad Nawfal, Amin H Nassar, Wanling Xie, Toni K Choueiri, Mark Pomerantz
The Oncologist.2024; 29(1): 8. CrossRef - Gene mutations as predictors of central lymph mode metastasis in cN0 PTC: A meta‐analysis
Jiaqi Ji, Xinlong Shi
Clinical Genetics.2024; 105(2): 130. CrossRef - Risk stratification by combining common genetic mutations and TERT promoter methylation in papillary thyroid cancer
Ye Sang, Guanghui Hu, Junyu Xue, Mengke Chen, Shubin Hong, Rengyun Liu
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Shortened telomere length in peripheral blood leukocytes is associated with cumulative radioactive iodine doses in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma
Hoonsung Choi, Sun Wook Cho, Hwan Hee Kim, Ka Hee Yi, Do Joon Park, Young Joo Park
Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - 2023 Update of the Korean Thyroid Association Guidelines for the Management of Thyroid Nodules
Eun Kyung Lee, Young Joo Park
Clinical Thyroidology®.2024; 36(4): 153. CrossRef - Deciphering the Functions of Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase in Head and Neck Cancer
Tsung-Jang Yeh, Chi-Wen Luo, Jeng-Shiun Du, Chien-Tzu Huang, Min-Hung Wang, Tzer-Ming Chuang, Yuh-Ching Gau, Shih-Feng Cho, Yi-Chang Liu, Hui-Hua Hsiao, Li-Tzong Chen, Mei-Ren Pan, Hui-Ching Wang, Sin-Hua Moi
Biomedicines.2023; 11(3): 691. CrossRef - 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Patients with Thyroid Nodules
Young Joo Park, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Soo Hwan Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Sun Wook Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Seung-Kuk Baek, So Won Oh, Min Kyoung Lee, Sang-Woo Lee, Young Ah Lee, Yong Sang Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Leehi Joo, Yuh-Seog Jung, Chan Kwon Jung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2023; 16(1): 1. CrossRef - Thyroid Cancer, Iodine, and Gene Mutation
Jae Hoon Chung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2023; 16(1): 89. CrossRef - Mortality rate and causes of death in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
Jung Heo, Hyun Jin Ryu, Hyunju Park, Tae Hyuk Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Young Lyun Oh, Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrine.2023; 83(3): 671. CrossRef - TERT promoter mutations in thyroid cancer
Michiko Matsuse, Norisato Mitsutake
Endocrine Journal.2023; 70(11): 1035. CrossRef - TERT Promoter and BRAF V600E Mutations in Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Single-Institution Experience in Korea
Min Jhi Kim, Jin Kyong Kim, Gi Jeong Kim, Sang-Wook Kang, Jandee Lee, Jong Ju Jeong, Woong Youn Chung, Daham Kim, Kee-Hyun Nam
Cancers.2022; 14(19): 4928. CrossRef - Frequency of TERT Promoter Mutations in Real-World Analysis of 2,092 Thyroid Carcinoma Patients (Endocrinol Metab 2022;37:652-63, Heera Yang et al.)
Hyunju Park, Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 949. CrossRef - Frequency of TERT Promoter Mutations in Real-World Analysis of 2,092 Thyroid Carcinoma Patients (Endocrinol Metab 2022;37:652-63, Heera Yang et al.)
Sue Youn Kim, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 947. CrossRef
-
TERT Promoter Mutations Frequency Across Race, Sex, and Cancer Type

- Calcium & Bone Metabolism
- Bone Mineral Density Screening Interval and Transition to Osteoporosis in Asian Women
- Hyunju Park, Heera Yang, Jung Heo, Hye Won Jang, Jae Hoon Chung, Tae Hyuk Kim, Yong-Ki Min, Sun Wook Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):506-512. Published online June 9, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1429

- 3,082 View
- 104 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Bone mineral density (BMD) testing is indicated for women aged 65 years, but screening strategies for osteoporosis are controversial. Currently, there is no study focusing on the BMD testing interval in Asian populations. The current study aimed to evaluate the estimated time interval for screening osteoporosis.
Methods
We conducted a study of 6,385 subjects aged 50 years and older who underwent dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry screening more than twice at Samsung Medical Center as participants in a routine health checkup. Subjects were divided based on baseline T-score into mild osteopenia (T-score, <–1.0 to >–1.5), moderate osteopenia (T-score, ≤–1.5 to >–2.0), and severe osteopenia (T-score, ≤–2.0 to >–2.5). Information about personal medical and social history was collected by a structured questionnaire.
Results
The adjusted estimated BMD testing interval for 10% of the subjects to develop osteoporosis was 13.2 years in mild osteopenia, 5.0 years in moderate osteopenia, and 1.5 years in severe osteopenia.
Conclusion
Our study provides extended information about BMD screening intervals in Asian female population. Baseline T-score was important for predicting BMD screening interval, and repeat BMD testing within 5 years might not be necessary in mild osteopenia subjects. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Bazedoxifene/Vitamin D Combination Therapy on Serum Vitamin D Levels and Bone Turnover Markers in Postmenopausal Women with Osteopenia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Chaiho Jeong, Jeonghoon Ha, Jun-Il Yoo, Young-Kyun Lee, Jung Hee Kim, Yong-Chan Ha, Yong-Ki Min, Dong-Won Byun, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ho Yeon Chung
Journal of Bone Metabolism.2023; 30(2): 189. CrossRef - Bone-modifying agents for non–small-cell lung cancer patients with bone metastases during the era of immune checkpoint inhibitors: A narrative review
Jinyoung Kim, Chaiho Jeong, Jeongmin Lee, Jeonghoon Ha, Ki-Hyun Baek, Seohyun Kim, Tai Joon An, Chan Kwon Park, Hyoung Kyu Yoon, Jeong Uk Lim
Seminars in Oncology.2023; 50(3-5): 105. CrossRef
- Effects of Bazedoxifene/Vitamin D Combination Therapy on Serum Vitamin D Levels and Bone Turnover Markers in Postmenopausal Women with Osteopenia: A Randomized Controlled Trial

- Clinical Study
- Economic Evaluation of Recombinant Human Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Stimulation vs. Thyroid Hormone Withdrawal Prior to Radioiodine Ablation for Thyroid Cancer: The Korean Perspective
- Seo Young Sohn, Hye Won Jang, Yoon Young Cho, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(4):531-542. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.4.531
- 3,552 View
- 43 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Previous studies have suggested that recombinant human thyroid stimulating hormone (rhTSH) stimulation is an acceptable alternative to thyroid hormone withdrawal (THW) when radioiodine remnant ablation is planned for thyroid cancer treatment, based on superior short-term quality of life with non-inferior remnant ablation efficacy. This study evaluated the cost-effectiveness of radioiodine remnant ablation using rhTSH, compared with the traditional preparation method which renders patients hypothyroid by THW, in Korean perspective.
Methods This economic evaluation considered the costs and benefits to the Korean public healthcare system. Clinical experts were surveyed regarding the current practice of radioiodine ablation in Korea and their responses helped inform assumptions used in a cost effectiveness model. Markov modelling with 17 weekly cycles was used to assess the incremental costs per quality-adjusted life year (QALY) associated with rhTSH. Clinical inputs were based on a multi-center, randomized controlled trial comparing remnant ablation success after rhTSH preparation with THW. The additional costs associated with rhTSH were considered relative to the clinical benefits and cost offsets.
Results The additional benefits of rhTSH (0.036 QALY) are achieved with an additional cost of Korean won ₩961,105, equating to cost per QALY of ₩26,697,361. Sensitivity analyses had only a modest impact upon cost-effectiveness, with one-way sensitivity results of approximately ₩33,000,000/QALY.
Conclusion The use of rhTSH is a cost-effective alternative to endogenous hypothyroid stimulation prior to radioiodine ablation for patients who have undergone thyroidectomy in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Recombinant Human Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone and Thyroid Hormone Withdrawal for 131I Therapy in Patients With Intermediate- to High-Risk Thyroid Cancer
Sohyun Park, Ji-In Bang, Keunyoung Kim, Youngduk Seo, Ari Chong, Chae Moon Hong, Dong-Eun Lee, Miyoung Choi, Sang-Woo Lee, So Won Oh
Clinical Nuclear Medicine.2024; 49(3): e96. CrossRef - Thyroid Hormone Withdrawal versus Recombinant Human TSH as Preparation for I-131 Therapy in Patients with Metastatic Thyroid Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Luca Giovanella, Maria Luisa Garo, Alfredo Campenní, Petra Petranović Ovčariček, Rainer Görges
Cancers.2023; 15(9): 2510. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life of thyroid cancer patients undergoing radioiodine therapy: a cohort real-world study in a reference public cancer hospital in Brazil
Jayda Eiras Ramim, Marcella Araugio Soares Cardoso, Gessen Lopes Carneiro de Oliveira, Maria Luisa Gomes, Tiago Teixeira Guimarães, Rossana Corbo Ramalho de Mello, Anke Bergmann, Priscilla Brunelli Pujatti
Supportive Care in Cancer.2020; 28(8): 3771. CrossRef - Predictive factors determining incomplete response to radioiodine therapy in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer
Ewelina Szczepanek-Parulska, Magdalena Wojewoda-Korbelak, Martyna Borowczyk, Malgorzata Kaluzna, Barbara Brominska, Katarzyna Ziemnicka, Rafal Czepczynski, Maciej Baczyk, Marek Ruchala
The Quarterly Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Initial Adoption of Recombinant Human Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Following Thyroidectomy in the Medicare Thyroid Cancer Patient Population
Michaela A. Dinan, Yanhong Li, Shelby D. Reed, Julie Ann Sosa
Endocrine Practice.2019; 25(1): 31. CrossRef - Triennial Report ofEndocrinology and Metabolism, 2015 to 2017
Eun-Jung Rhee, Hey Yeon Jang, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(2): 195. CrossRef - Recombinant human TSH stimulated thyroglobulin levels at remnant ablation predict structural incomplete response to treatment in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer
Jeonghoon Ha, Min Hee Kim, Kwanhoon Jo, Yejee Lim, Ja Seong Bae, Sohee Lee, Moo Il Kang, Bong Yun Cha, Dong Jun Lim
Medicine.2017; 96(29): e7512. CrossRef - Does the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome Increase in Thyroid Cancer Survivors?
Min-Hee Kim, Jin-young Huh, Dong-jun Lim, Moo-Il Kang
Thyroid.2017; 27(7): 936. CrossRef
- Comparison of Recombinant Human Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone and Thyroid Hormone Withdrawal for 131I Therapy in Patients With Intermediate- to High-Risk Thyroid Cancer

- Frequency of RAS Mutations and PAX8/PPARgamma Rearrangement in Follicular Thyroid Tumors in Korea.
- Hye Jeong Kim, Hye Won Jang, Seo Young Sohn, Yoon La Choi, Hee Jin Kim, Young Lyun Oh, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2012;27(1):45-53. Published online March 1, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2012.27.1.45
- 22,703 View
- 22 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Follicular thyroid tumors harbor several genetic alterations such as RAS mutations and PAX8/PPARgamma rearrangement. The aims of our study were to investigate the prevalence of RAS mutations and PAX8/PPARgamma rearrangement in follicular thyroid tumors and to correlate RAS mutations and/or PAX8/PPARgamma rearrangement with clinicopathologic features in Korean patients with follicular thyroid carcinomas. METHODS: RAS mutations were investigated by polymerase chain reaction and DNA sequencing in surgical specimens of 37 follicular thyroid carcinomas (FTCs) and 16 follicular thyroid adenomas (FTAs). PAX8/PPARgamma rearrangement was analyzed by fluorescent in situ hybridization in surgical specimens of 31 FTCs and 13 FTAs. RESULTS: RAS mutations were detected in 30% (11 of 37) of FTCs and 19% (three of 16) of FTAs. Three of 11 FTC patients with RAS mutations died of thyroid cancer, but none of the 26 FTC patients without RAS mutations. PAX8/PPARgamma rearrangement was found in 10% (three of 31) of FTCs, but in none of the 13 FTAs. All three FTC patients with PAX8/PPARgamma rearrangement remained in complete remission during follow-up. There were no FTC patients with both RAS mutations and PAX8/PPARgamma rearrangement. CONCLUSION: The prevalence of RAS mutations in our series of follicular tumors was similar to previous studies. The frequency of PAX8/PPARgamma rearrangements in our group of FTC was lower than previous western reports, but higher than Japanese reports. RAS mutations may be associated with hematogeneous metastasis and poor survival while PAX8/PPARgamma rearrangement may be related to more favorable prognosis in Korean patients with FTCs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preoperative serum thyroglobulin and changes in serum thyroglobulin during TSH suppression independently predict follicular thyroid carcinoma in thyroid nodules with a cytological diagnosis of follicular lesion
Hye Jeong Kim, Ji-Oh Mok, Chul Hee Kim, Yeo Joo Kim, Sang Jin Kim, Hyeong Kyu Park, Dong Won Byun, Kyoil Suh, Myung Hi Yoo
Endocrine Research.2017; 42(2): 154. CrossRef - Mutation Profile of Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer in Asians
Young Shin Song, Jung Ah Lim, Young Joo Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(3): 252. CrossRef - Analysis of RAS mutation and PAX8/PPARγ rearrangements in follicular-derived thyroid neoplasms in a Korean population: frequency and ultrasound findings
S. H. Jeong, H. S. Hong, J. J. Kwak, E. H. Lee
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2015; 38(8): 849. CrossRef
- Preoperative serum thyroglobulin and changes in serum thyroglobulin during TSH suppression independently predict follicular thyroid carcinoma in thyroid nodules with a cytological diagnosis of follicular lesion

- Clinicopathological Characteristics and Prognostic Factors of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma.
- Hye Won Jang, Ji In Lee, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Yong Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwang Won Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2010;25(3):183-191. Published online September 1, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2010.25.3.183
- 2,134 View
- 25 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Studies on the clinicopathological characteristics and prognostic factors of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) in Korea are very rare. METHODS: We enrolled 56 MTC patients who underwent surgery at Samsung Medical Center from 1995 to 2006. We analyzed their gender, age at diagnosis, the pathologic findings, the TNM stage, the association with multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN), RET protooncogene mutation and the, serum basal calcitonin levels before and after the surgery. We investigated the overall survival and the prognostic factors. RESULTS: The mean age at diagnosis was 46 years and the male/female ratio was 1:2.7. Fine needle aspiration cytology detected 61% of the MTC. The mean tumor size was 2.6 cm (range: 0.2-9.0 cm). Fifty-two percent of patients had the TNM stage more than III at the time of diagnosis. Distant metastasis was found in 5.3% (3/56) of the patients, either at the time of diagnosis or during the follow-up period. Hereditary MTC comprised of 23% of the patients and the disease developed at a younger age (38 years vs. 48 years, respectively, P < 0.05) with more bilaterality. RET protooncogene mutations were found in 27% (9/33) of the patients and most of them were in codon 634. After the primary surgery, the serum basal calcitonin levels were persistently elevated over 13 ng/L in 49% of the patients. The overall 5-year survival rate was 95.5%. Tumor size and distant metastasis were the significant prognostic factors for survival by univariate analysis (P < 0.05). CONCLUSION: There were no significant differences in the clinicopathological characteristics of MTC and survival in Korea compared to those of the Western countries. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preoperative Clinical and Sonographic Predictors for Lateral Cervical Lymph Node Metastases in Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Hye-Seon Oh, Hyemi Kwon, Eyun Song, Min Ji Jeon, Dong Eun Song, Tae Yong Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee, Suck Joon Hong, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Jung Hwan Baek, Won Gu Kim
Thyroid.2018; 28(3): 362. CrossRef - The Relationship between Ultrasonographic Features and Clinical Characteristics of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Min Joon Park, Young Sik Choi, Hee Sung Song, Beom Su Kim
Clinical Ultrasound.2018; 3(1): 8. CrossRef - Dynamic risk stratification for medullary thyroid cancer according to the response to initial therapy
Hyemi Kwon, Won Gu Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Dong Eun Song, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae-Yon Sung, Ki-Wook Chung, Jong Ho Yoon, Suck Joon Hong, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong
Endocrine.2016; 53(1): 174. CrossRef - Postoperative biochemical remission of serum calcitonin is the best predictive factor for recurrence‐free survival of medullary thyroid cancer: a large‐scale retrospective analysis over 30 years
Kyong Yeun Jung, Seok‐Mo Kim, Won Sang Yoo, Bup‐Woo Kim, Yong Sang Lee, Kyung Won Kim, Kyu Eun Lee, Jong Ju Jeong, Kee‐Hyun Nam, Se Hoon Lee, Jeong Hun Hah, Woong Youn Chung, Ka Hee Yi, Do Joon Park, Yeo‐Kyu Youn, Myung‐Whun Sung, Bo Youn Cho, Cheong Soo
Clinical Endocrinology.2016; 84(4): 587. CrossRef - Changing trends in the clinicopathological features and clinical outcomes of medullary thyroid carcinoma
Hyemi Kwon, Won Gu Kim, Tae‐Yon Sung, Min Ji Jeon, Dong Eun Song, Yu‐Mi Lee, Jong Ho Yoon, Ki‐Wook Chung, Suck Joon Hong, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Journal of Surgical Oncology.2016; 113(2): 152. CrossRef - Localization of medullary thyroid carcinoma after surgery using 11C-methionine PET/CT: comparison with 18F-FDG PET/CT
Hye Won Jang, Joon Young Choi, Ji In Lee, Hee Kyung Kim, Hyun Won Shin, Jung Hee Shin, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrine Journal.2010; 57(12): 1045. CrossRef
- Preoperative Clinical and Sonographic Predictors for Lateral Cervical Lymph Node Metastases in Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma

- Clinico-pathologic Characteristics of the Primary Thyroid Cancer in Patients with Breast Cancer.
- Hyun Won Shin, Hye Won Jang, Ji Young Park, Jae Hoon Chung, Young Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwang Won Kim, Sun Wook Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2009;24(4):240-246. Published online December 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2009.24.4.240
- 2,142 View
- 27 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Both thyroid and breast cancers occur more frequently in women than in men. Some suggest that estrogen plays a role in the tumorigenesis of both cancers. The aim of this study was to identify the prevalence and clinico-pathologic characteristics of primary thyroid cancer in patients with breast cancer. METHODS: We retrospectively obtained clinical and pathologic data for 112 patients diagnosed with both thyroid and breast cancer from a single center. Patients with thyroid cancer were grouped according to the chronological sequence of tumor diagnosis. When thyroid and breast cancers were diagnosed within 12 months of each other, they were considered to have been diagnosed simultaneously. Female patients who had only papillary thyroid cancer were used as a historic control. RESULTS: Between 1994 and 2008, 7,827 patients at our hospital were diagnosed with breast cancer and 6,571 patients with thyroid cancer. There were 112 patients who had both thyroid and breast cancer. All thyroid cancers (111/112) except one hurthle cell cancer were papillary thyroid cancers. Average tumor size of thyroid cancer cases diagnosed 1) after or 2) simultaneously with the diagnosis of breast cancer was significantly lower than that for 3) thyroid cancer cases found before breast cancer diagnosis or 4) historical controls with papillary thyroid cancer [sizes (in cm), respectively, were: 1) 0.9 +/- 0.6 2) 0.9 +/- 0.5 vs 3) 1.4 +/- 0.9 4) 1.4 +/- 1.1, P < 0.05]. No patients had distant metastases and there were no statistically significant differences in known risk factors for recurrence and survival of patients with thyroid cancer. CONCLUSION: Thyroid cancer is the most common second primary malignancy in patients with breast cancer and most of them are papillary thyroid cancers. There are no differences in risk factors for tumor recurrence and patient survival compared with those with conventional papillary thyroid cancer except for differences in tumor size. These difference in size may reflect an increase in medical surveillance in patients after they are diagnosed with breast cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Survival Outcomes in Thyroid Cancer Patients with Co-Occurring Breast Cancer: Evidence of Mortality Risk Attenuation
Matheus Wohlfahrt Baumgarten, Iuri Martin Goemann, Rafael Selbach Scheffel, Ana Luiza Maia
Clinical Breast Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The prognosis and treatment of primary thyroid cancer occurred in breast cancer patients: comparison with ordinary thyroid cancer
Chang Min Park, Young Don Lee, Eun Mee Oh, Kwan-Il Kim, Heung Kyu Park, Kwang-Pil Ko, Yoo Seung Chung
Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research.2014; 86(4): 169. CrossRef - Thyroid Metastasis from Breast Carcinoma Accompanied by Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Song-I Yang, Kwang-Kuk Park, Jeong-Hoon Kim
Case Reports in Oncology.2014; 7(2): 528. CrossRef
- Survival Outcomes in Thyroid Cancer Patients with Co-Occurring Breast Cancer: Evidence of Mortality Risk Attenuation

- Clinical Differences between Classic Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and Variants.
- Ji Young Park, Ji In Lee, Alice Hyun Kyung Tan, Hye Won Jang, Hyun Won Shin, Young Lyun Oh, Jung Hee Shin, Jung Han Kim, Ji Soo Kim, Young Ik Son, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2009;24(3):165-173. Published online September 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2009.24.3.165
- 2,051 View
- 22 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The outcomes of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) variants have been described in a limited number of studies. The purpose of this study was to compare patient outcomes of PTC variants with those of patients with classic PTC. METHODS: A single-institution retrospective analysis was performed to review 2,366 patients with classic PTC and 159 patients with PTC variants diagnosed between 1994 and 2004. PTC variant patients were divided into two groups, favorable (n = 119, 119 follicular variants including 14 encapsulated follicular variants) and aggressive (n = 40, including 13 diffuse sclerosing, 11 tall cell, six solid, six oncocytic, and four columnar cell variants). RESULTS: Compared with classic PTC, the favorable and aggressive variants had a significantly larger tumor size (P<0.001). The favorable variants had significantly lower rates of bilaterality, multifocality, extrathyroidal invasion, cervical lymph node metastasis, stage III and IV disease, and greater male to female ratio (P<0.05). In particular, the encapsulated follicular variant showed no bilaterality, multifocality, extrathyroidal invasion, lymph node metastasis, and distant metastasis. However, the disease-specific survival and recurrence-free survival of patients with favorable PTC were not different from the patients with classic PTC. The aggressive variants had significantly higher rates of bilaterality and cervical lymph node metastasis compared to the classic PTC (P<0.05). They had significantly reduced disease-specific survival and recurrence-free survival rates (P<0.01). CONCLUSIONS: Knowledge of the nature of PTC variants, especially aggressive types, is important in predicting patient outcome and providing appropriate treatment. Further study is needed to better understand PTC variants. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultrasonographic Characteristics of the Follicular Variant Papillary Thyroid Cancer According to the Tumor Size
Eon Ju Jeon, Young Ju Jeong, Sung Hwan Park, Chang Ho Cho, Ho Sang Shon, Eui Dal Jung
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2016; 31(3): 397. CrossRef - Follicular Variant of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Distinct Biologic Behavior Based on Ultrasonographic Features
Sun Jung Rhee, Soo Yeon Hahn, Eun Sook Ko, Jae Wook Ryu, Eun Young Ko, Jung Hee Shin
Thyroid.2014; 24(4): 683. CrossRef
- Ultrasonographic Characteristics of the Follicular Variant Papillary Thyroid Cancer According to the Tumor Size

- Search for Materials that Influence Human Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Cell Proliferation.
- Hyun Won Shin, Hye Won Jang, Keun Sook Kim, Ji In Lee, Ji Young Park, Sun Wook Kim, Yong Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwang Won Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2009;24(2):93-99. Published online June 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2009.24.2.93
- 2,060 View
- 20 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Surgical excision is the only effective treatment of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) and there is no certain treatment for recurrence or distant metastasis. Materials that influence MTC cell proliferation were recently reported. Presently, we evaluated the influence of dexamethasone, somatostatin, progesterone, estradiol-17-beta, forskolin and gastrin on MTC cell proliferation and calcitonin secretion. METHODS: Genomic DNA was extracted and sequenced from untreated thyroid TT cells and cells treated with 10-5~10-10 M dexamethasone, somatostatin, progesterone, estradiol-17-beta, forskolin or gastrin, and cultured for 1~6 days. Cell proliferation was assessed using a BrdU assay at days 1, 2, 3, and 6. Calcitonin in the culture medium from dexamethasone-treated TT cells was measured at days 1~3. RESULTS: Replacement of cysteine with tryptophan at codon 634 of exon 11 was evident in treated TT cells. There was no significant difference in cell proliferation at days 1~3 in cells treated with somatostatin, progesterone, estradiol-17-beta, gastrin and forskolin, while proliferation was inhibited in dexamethasone-treated cells in a concentration-dependent manner from 10-5~10-8 M with no inhibition evident at 10-10 M. Calcitonin levels in 10-5~10-8 M dexamethasone-treated cells were decreased. CONCLUSION: Dexamethasone is a potentially useful compound to suppress MTC cell proliferation. Further studies are necessary to explore this potential further prior to clinical use. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Identification of Growth Regulatory Factors in Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Cell Line
Young Suk Jo, Minho Shong
Journal of Korean Endocrine Society.2009; 24(2): 84. CrossRef
- Identification of Growth Regulatory Factors in Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Cell Line

- A Case of Hyalinizing Trabecular Adenoma of the Thyroid Gland.
- Hyun Won Shin, Young Lyun Oh, Hye Won Jang, Ji In Lee, Sun Wook Kim, Yong Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwang Won Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2009;24(1):54-57. Published online March 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2009.24.1.54
- 2,062 View
- 19 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hyalinizing trabecular tumor is a rare benign thyroid tumor first described by Carney et al. in 1987. The tumor is characterized by an encapsulated nodule, trabecular arrangement of polygonal, oval, elongated cells, and hyalinized stroma. It is easily confused with papillary thyroid carcinoma or medullary thyroid carcinoma on surgical and cytologic specimens. A 45-year-old man presented with an incidentally detected left thyroid mass. Fine needle aspiration was performed and papillary thyroid carcinoma was suspected. However, the surgical specimen revealed a hyalinizing trabecular adenoma. We present this hyalinizing trabecular adenoma case to share our experience with physicians and specialists.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Case of Multifocal Hyalinizing Trabecular Tumors of the Thyroid
Gland
Suhwan Jeong, Hanaro Park
Journal of Clinical Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery.2021; 32(3): 308. CrossRef - A Case of Hyalinizing Trabecular Tumor of the Thyroid Gland
Kun Woo Kim, Sang Joon Lee, Phil-Sang Chung, Junghwan Moon
Korean Journal of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery.2012; 55(12): 795. CrossRef
- A Case of Multifocal Hyalinizing Trabecular Tumors of the Thyroid
Gland

- ras Mutation in Korean Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas.
- Jung Hwa Jung, Keun Sook Kim, Tae Sik Jung, Young Lyun Oh, Hye Won Jang, Hye Seung Jung, Yong Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Kwang Won Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2007;22(3):203-209. Published online June 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2007.22.3.203
- 1,838 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
RET/PTC rearrangement and mutations of BRAF and ras are well-known oncogenes involved in the pathogenesis of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). The prevalence of RET/PTC rearrangement and BRAF mutations were 0~13% and 66~83% in Korean patients with PTC, respectively. We evaluated the prevalence of ras mutations in surgical specimens of PTC, and we compared them with the patients' clinical features. SUBJECTS AND METHODS: We included the surgical specimens of 49 PTCs and a few follicular thyroid carcinomas (FTCs) and follicular adenomas (FAs) as positive controls. Polymerase chain reaction, single strand conformation polymorphism and direct sequence analysis were consecutively performed to detect ras mutations. RESULTS: No mutations of the ras oncogenes were detected in 49 PTCs. However, heterozygous mutations of the ras oncogenes were found in a FTC and FA as positive controls, respectively. CONCLUSION: These findings suggested that ras mutation is not or rarely related to the tumorigenesis of PTCs in Koreans. Therefore, BRAF mutations and RET/PTC rearrangement, rather than ras mutation, might contribute the development of PTC in Koreans.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



